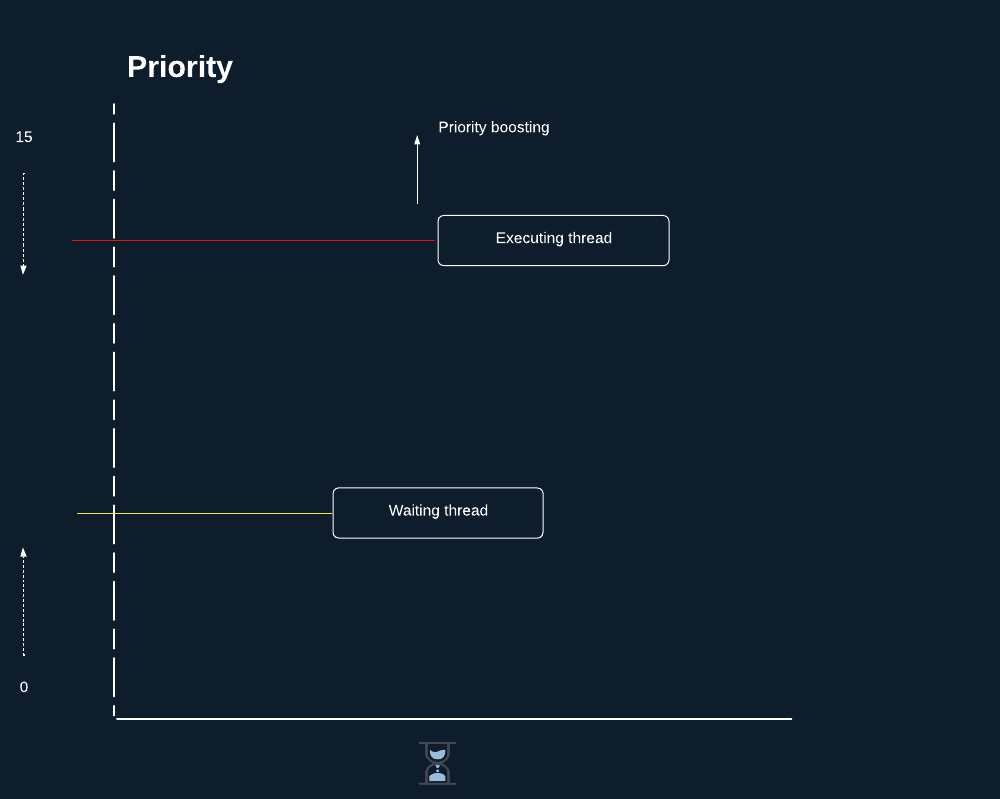
Priority boosting is an internal mechanism used by the Windows scheduler to dynamically adjust the current priority of threads, either increasing or decreasing it, to minimize certain latencies and enhance responsiveness to events that threads are waiting for (e.g., user input or the completion of I/O operations). Notably, Windows never boosts the priority of threads within the real-time range (16–31).The algorithm that Windows uses for thread scheduling is priority-driven and, in some cases, incorporates a round-robin method.
